Understanding the Factors That Influence Vaccine Hesitancy
Project Team
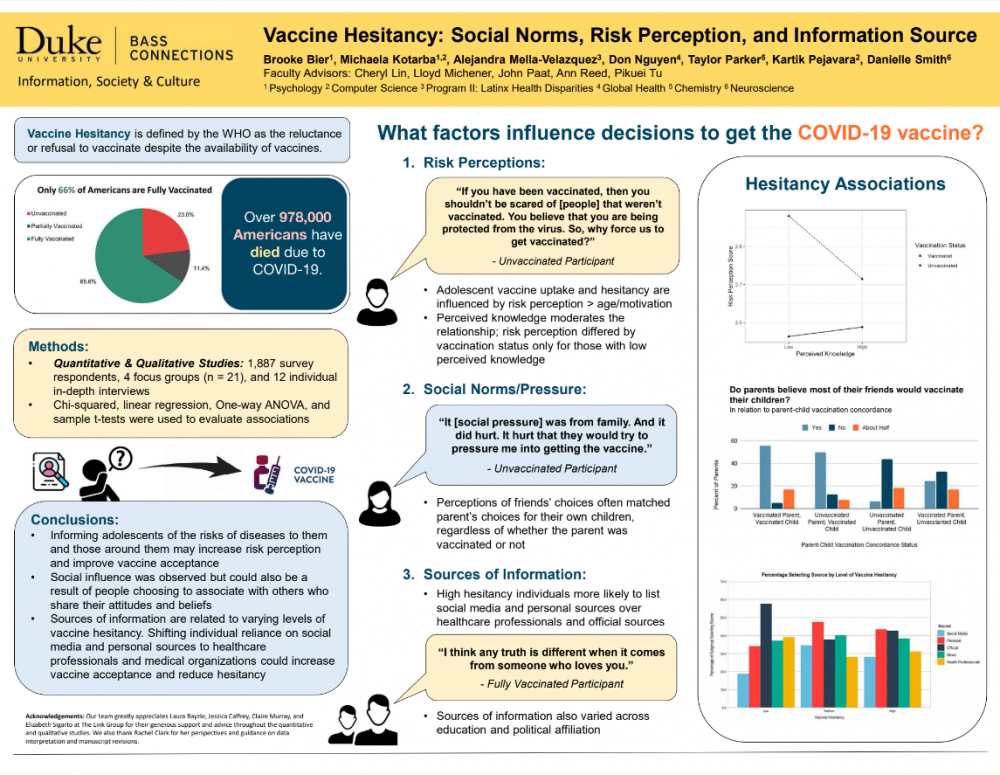
Health decisions and behaviors are influenced by information access, cultural and social norms, and policies that may elicit acceptance or resistance. For example, vaccines have been a savior invention for individual health and the greater society, but doubts about vaccines’ necessity, efficacy and safety have endured since the 1800s. Misinformation and antivaccine sentiments in recent years have caused resurgences of diseases that were eliminated or nearly eradicated.
The current COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the issue of widespread vaccine hesitancy, defined by the World Health Organization as the reluctance or refusal to vaccinate despite the availability of vaccines. The team used surveys, focus groups and in-depth individual interviews to determine the factors that may be affecting levels of hesitancy, including risk perception, social norms and sources of information. Their work offered policymakers comprehensive, up-to-date insights and recommendations for planning, executing and monitoring immunization programs.
Vaccine Hesitancy: Social Norms, Risk Perception, and Information Source
Poster by Brooke Bier, Michaela Kotarba, Alejandra Mella-Velazquez, Don Nguyen, Taylor Parker, Kartik Pejavara and Danielle Smith